Embark on a journey into the realm of atomic structure with our engaging electron configuration and orbital notation worksheet. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to decipher the electronic configurations of elements, unlocking the secrets of their chemical behavior.
Delve into the fundamental concepts of electron configuration, unraveling the Aufbau principle and Pauli exclusion principle. Explore the fascinating world of orbitals, discovering their shapes and significance. Our worksheet provides a hands-on approach, guiding you through exercises that reinforce your understanding.
Electron Configuration and Orbital Notation
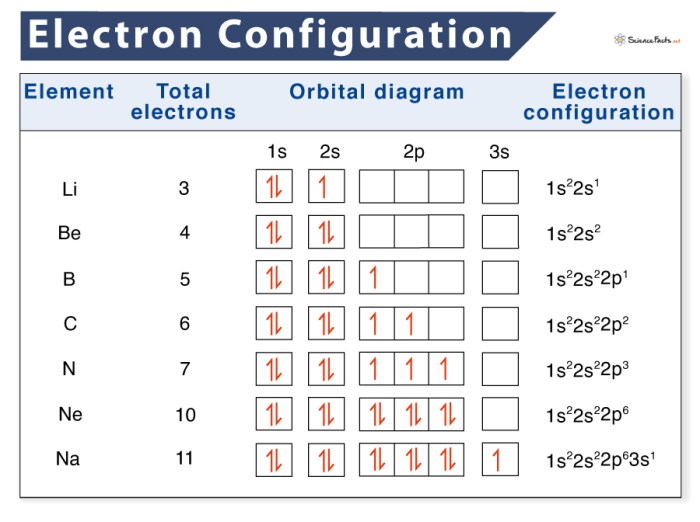
Electron configuration and orbital notation are two important concepts in chemistry that describe the arrangement of electrons in atoms. Electron configuration refers to the distribution of electrons in different energy levels and orbitals around the atomic nucleus, while orbital notation is a way of representing the electron configuration using symbols.
Understanding electron configuration and orbital notation is essential for comprehending the chemical properties of elements and their behavior in chemical reactions.
Electron Configuration, Electron configuration and orbital notation worksheet
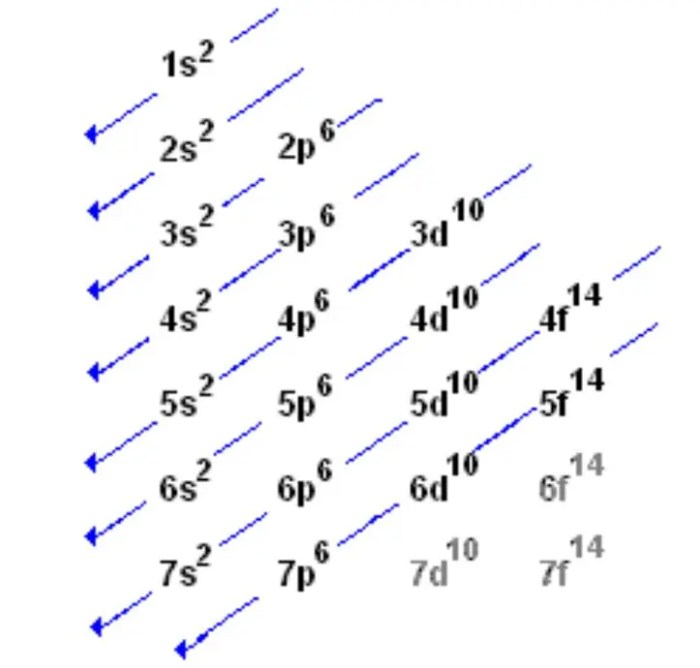
Electron configuration is the distribution of electrons in different energy levels and orbitals around the atomic nucleus. The energy levels are labeled as 1, 2, 3, …, and the orbitals within each energy level are labeled as s, p, d, and f.
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first. The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers.
Table of Electron Configuration
| Element | Atomic Number | Electron Configuration | Orbital Diagram ||—|—|—|—|| Hydrogen | 1 | 1s 1|  || Helium | 2 | 1s 2|
|| Helium | 2 | 1s 2|  || Lithium | 3 | 1s 22s 1|
|| Lithium | 3 | 1s 22s 1|  || … | … | … | … |
|| … | … | … | … |
Orbital Notation
Orbital notation is a way of representing the electron configuration using symbols. The symbols represent the type of orbital (s, p, d, or f) and the number of electrons in that orbital. For example, the orbital notation for the electron configuration 1s 22s 22p 63s 23p 3would be:“`
s22s 22p 63s 23p 3
↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑“`The arrows represent the spin of the electrons.
Table of Orbital Types
| Orbital Type | Shape | Number of Electrons | Examples ||—|—|—|—|| s | Spherical | 2 | 1s, 2s, 3s || p | Dumbbell | 6 | 2p x, 2p y, 2p z|| d | Complex | 10 | 3d xy, 3d yz, 3d zx, 3d x2-y 2, 3d z2|| f | Complex | 14 | 4f xyz, 4f x(x2-3y 2) , 4f y(3x2-y 2) , … |
Rules for Writing Orbital Notation
- The number of electrons in each orbital must be less than or equal to the maximum number of electrons that can occupy that orbital.
- The electrons must be filled in the lowest energy orbitals first.
- The electrons must be paired in orbitals with the same spin whenever possible.
FAQ Section: Electron Configuration And Orbital Notation Worksheet
What is electron configuration?
Electron configuration refers to the distribution of electrons in different energy levels and orbitals around an atomic nucleus.
How does the Aufbau principle guide electron configuration?
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy, starting with the lowest energy level.
What is the significance of the Pauli exclusion principle?
The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.