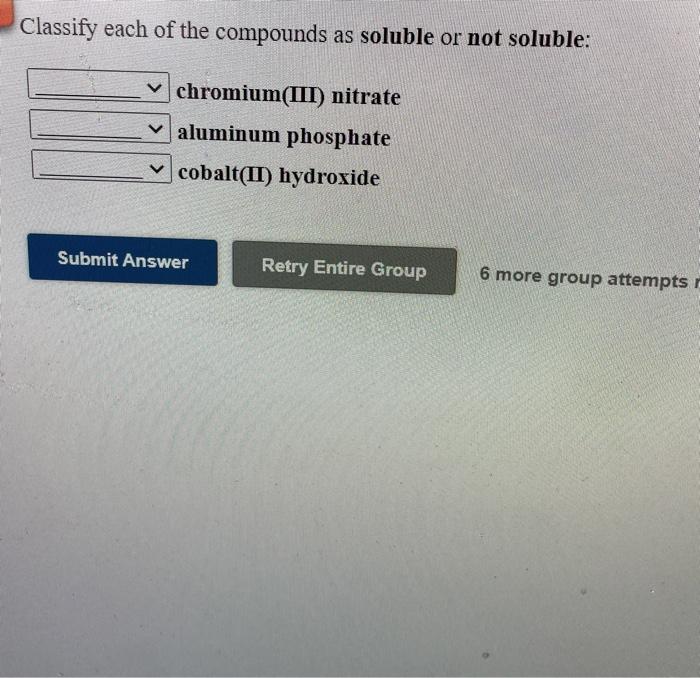
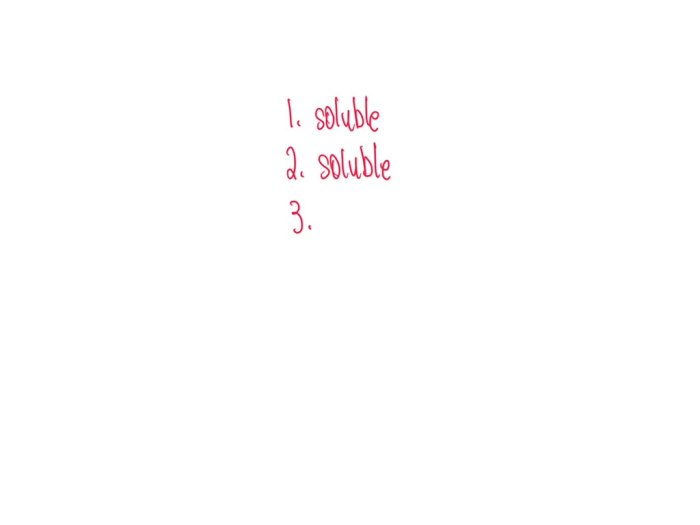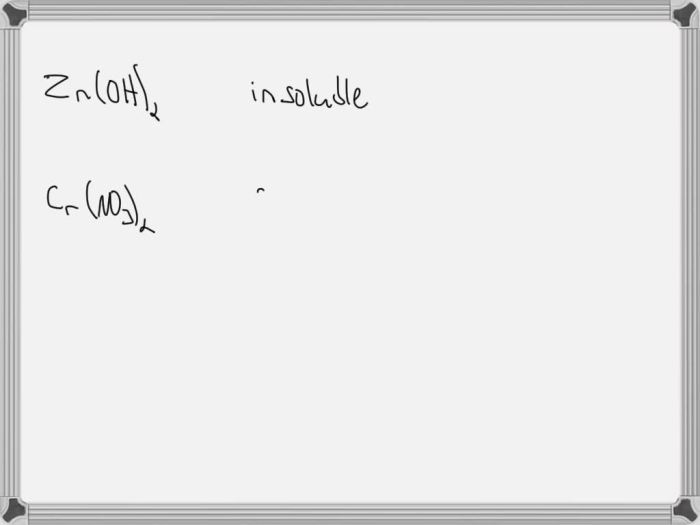Classify each of the compounds as soluble or not soluble – Embark on a scientific journey to classify compounds as soluble or insoluble. This guide unravels the intricacies of solubility, equipping you with a comprehensive understanding of its concepts, factors, rules, and applications.
Solubility, the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, plays a pivotal role in numerous fields, from chemistry and drug development to environmental monitoring. By delving into the factors influencing solubility, such as temperature, pressure, and solvent properties, we gain insights into the behavior of compounds in different environments.
Solubility of Compounds
Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent to form a homogeneous mixture. A substance that dissolves is called soluble, while a substance that does not dissolve is called insoluble.
Solubility is an important property in various fields, such as chemistry, pharmacy, and environmental science. It plays a crucial role in chemical reactions, drug development, and environmental monitoring.
Factors Affecting Solubility
The solubility of a compound is influenced by several factors, including:
- Temperature:Generally, the solubility of solids in liquids increases with increasing temperature. However, the solubility of gases in liquids decreases with increasing temperature.
- Pressure:The solubility of gases in liquids increases with increasing pressure. This relationship is described by Henry’s law.
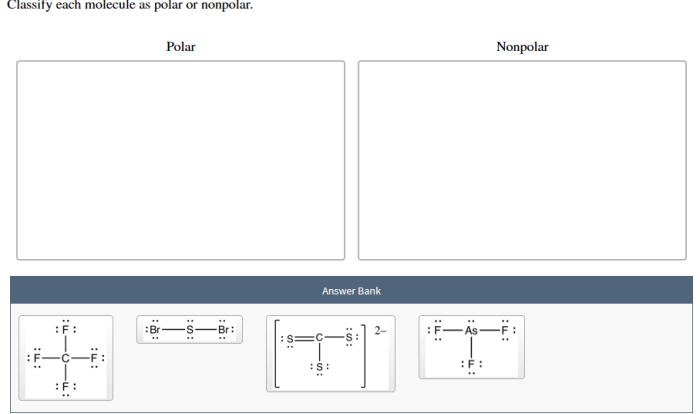
- Solvent properties:The nature of the solvent can significantly affect the solubility of a compound. Polar solvents tend to dissolve polar compounds, while nonpolar solvents tend to dissolve nonpolar compounds.
Solubility Rules, Classify each of the compounds as soluble or not soluble
General solubility rules provide guidelines for predicting the solubility of common types of compounds:
- Ionic compounds:Most ionic compounds are soluble in water, except for some sulfates, carbonates, and phosphates.
- Covalent compounds:Covalent compounds are generally insoluble in water unless they contain polar functional groups, such as hydroxyl (-OH) or carboxyl (-COOH) groups.
- Organic compounds:Organic compounds are typically insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar organic solvents.
Applications of Solubility
Solubility has numerous practical applications, including:
- Chemical separations:Solubility differences can be used to separate compounds in a mixture by techniques such as precipitation and extraction.
- Drug development:Solubility is a crucial factor in determining the bioavailability and efficacy of drugs.
- Environmental monitoring:Solubility data is used to assess the fate and transport of pollutants in the environment.
Top FAQs: Classify Each Of The Compounds As Soluble Or Not Soluble
What is the difference between soluble and insoluble compounds?
Soluble compounds dissolve in a solvent to form a homogeneous mixture, while insoluble compounds do not dissolve and form a heterogeneous mixture.
What factors affect the solubility of a compound?
Temperature, pressure, solvent properties, and the nature of the solute all influence the solubility of a compound.
What are the general solubility rules for ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds containing Group 1 cations (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, Cs+) and Group 2 cations (Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+) are generally soluble in water. Compounds containing nitrate (NO3-), chloride (Cl-), bromide (Br-), or iodide (I-) anions are also typically soluble.