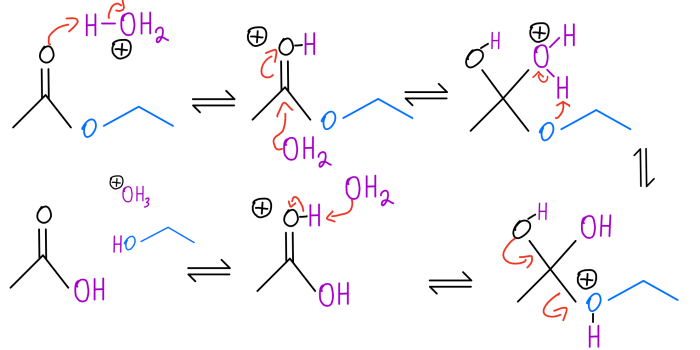
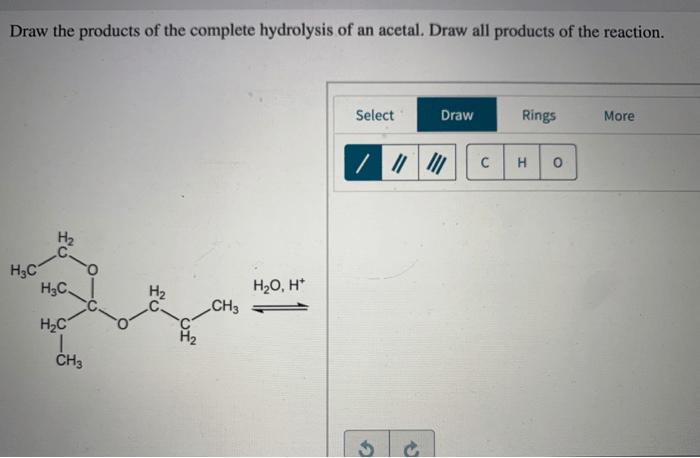
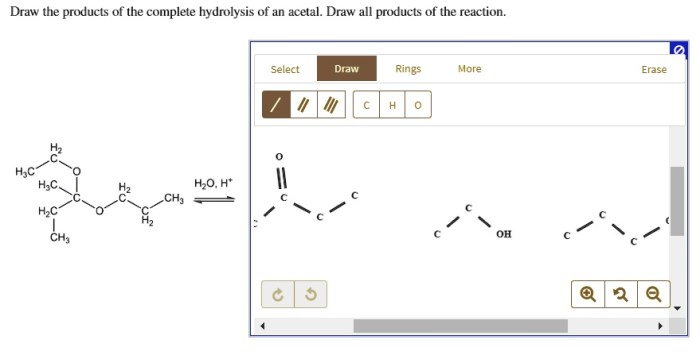
Draw the products of the complete hydrolysis of an acetal, an essential reaction in organic chemistry. This process involves the cleavage of the acetal functional group, yielding two alcohol molecules and a carbonyl compound. Understanding the mechanism, products, and applications of acetal hydrolysis is crucial for various fields, including organic synthesis, biochemistry, and industrial chemistry.
Acetals are functional groups commonly found in organic compounds. They consist of two alkoxy groups attached to a central carbon atom. Upon hydrolysis, acetals undergo a nucleophilic attack by water, leading to the breaking of the carbon-oxygen bond and the formation of two alcohol molecules and a carbonyl compound, typically an aldehyde or ketone.
Hydrolysis of Acetals
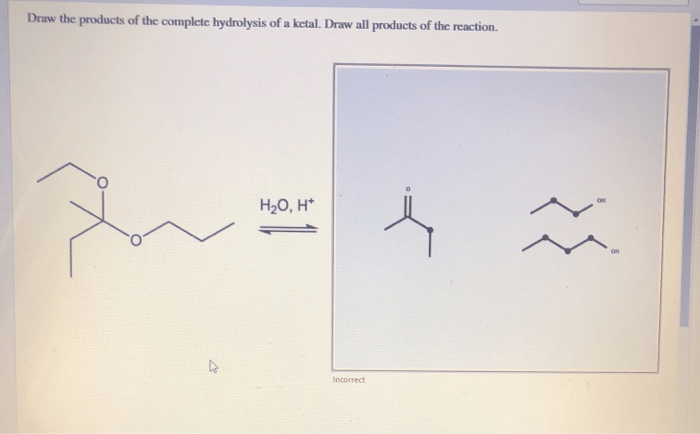
Acetals are organic compounds that contain two alkoxy groups attached to a carbon atom. They are formed by the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. Acetals are hydrolyzed back to the corresponding aldehyde or ketone and alcohol in the presence of an acid or base catalyst.The
mechanism of acetal hydrolysis involves the protonation of the acetal oxygen by the acid catalyst, followed by nucleophilic attack by water. This results in the formation of a hemiacetal intermediate, which is then protonated and hydrolyzed to give the aldehyde or ketone and alcohol products.
Examples of Acetal Hydrolysis Reactions, Draw the products of the complete hydrolysis of an acetal
The hydrolysis of acetals is a versatile reaction that can be used to synthesize a variety of aldehydes and ketones. Some examples of acetal hydrolysis reactions include:
- The hydrolysis of dimethyl acetal to give formaldehyde and methanol
- The hydrolysis of diethyl acetal to give acetaldehyde and ethanol
- The hydrolysis of benzaldehyde dimethyl acetal to give benzaldehyde and methanol
Role of Acid or Base Catalysts in Acetal Hydrolysis
Acetal hydrolysis can be catalyzed by both acid and base catalysts. Acid catalysts, such as hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid, protonate the acetal oxygen and facilitate the nucleophilic attack by water. Base catalysts, such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, deprotonate the acetal oxygen and make it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack by water.
Products of Acetal Hydrolysis
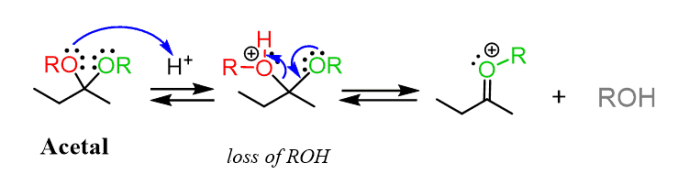
The products of complete hydrolysis of an acetal are an aldehyde or ketone and an alcohol. The aldehyde or ketone product is formed by the cleavage of the carbon-oxygen bond between the acetal carbon and the alkoxy group. The alcohol product is formed by the cleavage of the carbon-oxygen bond between the acetal carbon and the other alkoxy group.The
formation of these products can be explained by the mechanism of acetal hydrolysis. The protonation of the acetal oxygen by the acid catalyst makes the carbon-oxygen bond between the acetal carbon and the alkoxy group more susceptible to nucleophilic attack by water.
This results in the formation of a hemiacetal intermediate, which is then protonated and hydrolyzed to give the aldehyde or ketone and alcohol products.
Relationship between the Structure of the Acetal and the Products of Hydrolysis
The structure of the acetal affects the products of hydrolysis. Acetals that are derived from symmetrical aldehydes or ketones will give symmetrical products upon hydrolysis. For example, the hydrolysis of dimethyl acetal will give formaldehyde and methanol, both of which are symmetrical molecules.Acetals
that are derived from unsymmetrical aldehydes or ketones will give unsymmetrical products upon hydrolysis. For example, the hydrolysis of diethyl acetal will give acetaldehyde and ethanol, which are both unsymmetrical molecules.
Applications of Acetal Hydrolysis
Acetal hydrolysis is a useful reaction in a variety of industrial and laboratory applications. Some examples of the applications of acetal hydrolysis include:
- The production of aldehydes and ketones. Acetal hydrolysis is used to produce a variety of aldehydes and ketones, which are used in the manufacture of perfumes, flavors, and pharmaceuticals.
- The synthesis of organic compounds. Acetal hydrolysis is used to synthesize a variety of organic compounds, including esters, amides, and imines.
- The protection of aldehydes and ketones. Acetals are used to protect aldehydes and ketones from nucleophilic attack. This is useful in a variety of reactions, such as the Grignard reaction and the Diels-Alder reaction.
Experimental Procedures for Acetal Hydrolysis
Acetal hydrolysis can be carried out in a variety of ways. The most common method is to heat the acetal in the presence of an acid or base catalyst. The reaction can be monitored by thin-layer chromatography or gas chromatography.The
following is a general procedure for the hydrolysis of an acetal:
- Dissolve the acetal in a suitable solvent, such as methanol or ethanol.
- Add a catalytic amount of an acid or base catalyst.
- Heat the reaction mixture to reflux.
- Monitor the reaction by thin-layer chromatography or gas chromatography.
- Once the reaction is complete, cool the reaction mixture and extract the products with a suitable organic solvent.
- Dry the organic extract over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrate it under reduced pressure.
- Purify the products by distillation or crystallization.
Safety Precautions for Conducting Acetal Hydrolysis Experiments
Acetal hydrolysis experiments should be conducted in a well-ventilated area. The following safety precautions should be followed:
- Wear gloves and safety glasses.
- Use a fume hood when working with volatile solvents.
- Keep all flammable materials away from the reaction.
- Do not heat the reaction mixture above its boiling point.
- If the reaction mixture catches fire, smother it with a fire extinguisher.
FAQ Summary: Draw The Products Of The Complete Hydrolysis Of An Acetal
What is the mechanism of acetal hydrolysis?
Acetal hydrolysis proceeds via a nucleophilic attack by water on the acetal carbon, leading to the breaking of the carbon-oxygen bond and the formation of two alcohol molecules and a carbonyl compound.
What are the products of acetal hydrolysis?
The products of acetal hydrolysis are two alcohol molecules and a carbonyl compound, typically an aldehyde or ketone.
What is the role of acid or base catalysts in acetal hydrolysis?
Acid or base catalysts can accelerate the rate of acetal hydrolysis by providing protons or hydroxide ions, respectively, which facilitate the nucleophilic attack by water.