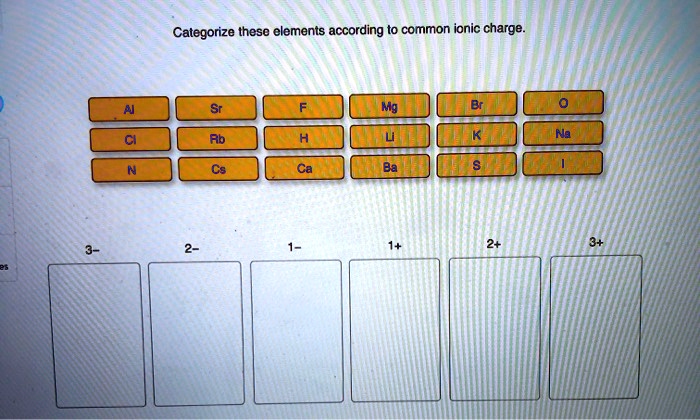
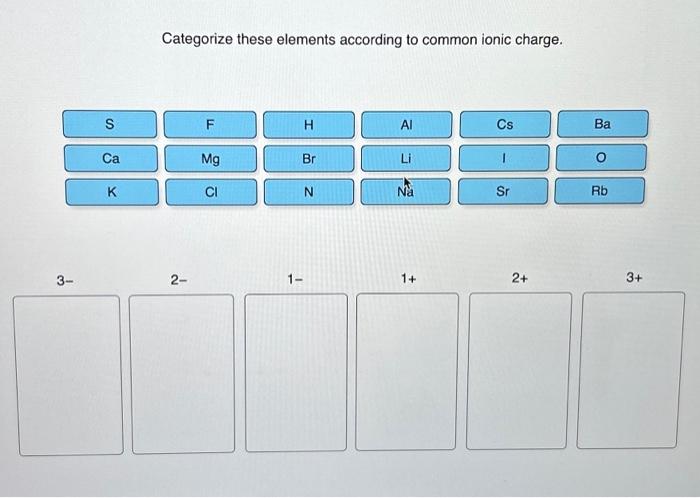
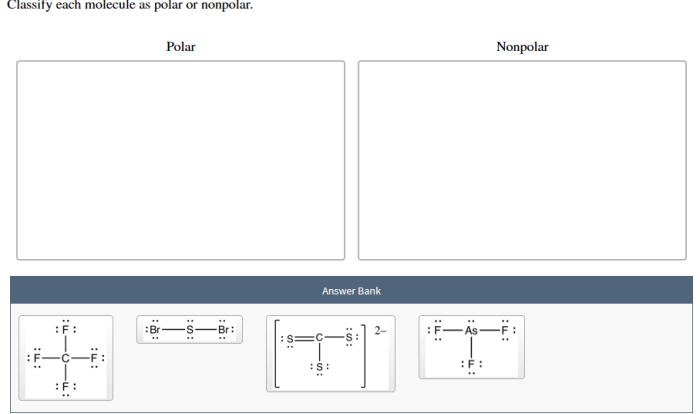
Categorize these elements according to common ionic charge sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating realm of ionic charges, exploring their significance and providing a systematic approach to categorizing elements based on this fundamental property.
Ionic charges play a pivotal role in shaping the behavior of elements, influencing their chemical reactivity, physical properties, and countless applications across diverse scientific disciplines. By understanding the common ionic charges associated with different elements, we gain a deeper comprehension of the periodic table and the intricate dance of electrons that governs the interactions between atoms.
Categorizing Elements According to Common Ionic Charge: Categorize These Elements According To Common Ionic Charge

Ionic charge is a fundamental property of elements that plays a crucial role in their chemical behavior. By categorizing elements based on their ionic charge, scientists can gain insights into their reactivity, bonding properties, and potential applications.
In this article, we will explore the different types of ionic charges, methods for categorizing elements based on their ionic charge, and the practical applications of this categorization.
Types of Ionic Charges
- Positive Ionic Charge:Elements that have lost one or more electrons and have a net positive charge are known as cations. The positive ionic charge is typically represented by a superscript number after the element symbol, indicating the number of electrons lost.
- Negative Ionic Charge:Elements that have gained one or more electrons and have a net negative charge are known as anions. The negative ionic charge is also represented by a superscript number after the element symbol, preceded by a minus sign.
The ionic charge of an element is determined by the number of protons and electrons it contains. When the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons, the element has a neutral charge. However, when the number of protons is greater than the number of electrons, the element has a positive charge (cation), and when the number of protons is less than the number of electrons, the element has a negative charge (anion).
Methods for Categorizing Elements by Ionic Charge, Categorize these elements according to common ionic charge
There are several methods used to categorize elements based on their ionic charge, including:
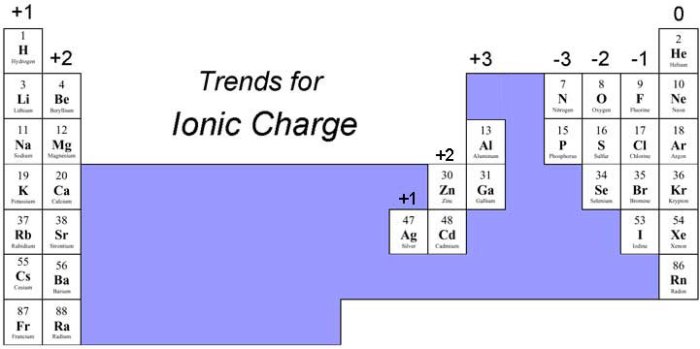
- Periodic Table Groups:Elements in the same group of the periodic table typically have the same ionic charge. For example, all alkali metals (Group 1) form cations with a +1 charge, while all halogens (Group 17) form anions with a -1 charge.
- Electron Configuration:The electron configuration of an element can also be used to determine its ionic charge. Elements that have a stable electron configuration with a full or half-filled outermost shell tend to form ions with charges that result in a stable electron configuration.
- Oxidation States:Oxidation states represent the hypothetical charge of an element in a compound. They can be used to determine the ionic charge of an element in a particular compound.
Applications of Categorizing Elements by Ionic Charge
Categorizing elements by their ionic charge has several practical applications, including:
- Predicting Chemical Reactivity:The ionic charge of an element can help predict its chemical reactivity. For example, elements with a high positive charge tend to be more reactive than elements with a low positive charge.
- Designing Materials:The ionic charge of elements is a key factor in determining the properties of materials. For example, materials with a high concentration of ions with opposite charges tend to be more brittle than materials with a low concentration of ions.
- Understanding Biological Processes:The ionic charge of elements plays a crucial role in many biological processes, such as nerve transmission and muscle contraction.
Limitations and Exceptions
While categorizing elements by their ionic charge is a useful tool, there are some limitations and exceptions to consider:
- Variable Ionic Charges:Some elements can exhibit multiple ionic charges. For example, iron can form cations with charges of +2 and +3.
- Covalent Bonding:In some cases, elements can form covalent bonds, where electrons are shared between atoms, rather than forming ions. In these cases, the concept of ionic charge may not be applicable.
- Factors Influencing Ionic Charge:The ionic charge of an element can be influenced by factors such as the surrounding environment, temperature, and pressure.
Clarifying Questions
What are the most common ionic charges?
The most common ionic charges are +1, +2, +3, -1, and -2.
How do I determine the ionic charge of an element?
The ionic charge of an element can be determined by subtracting the number of electrons in the element’s neutral state from the number of protons in its nucleus.
What is the relationship between ionic charge and chemical reactivity?
Ionic charge plays a significant role in chemical reactivity, as it influences the electrostatic interactions between ions and other atoms or molecules.