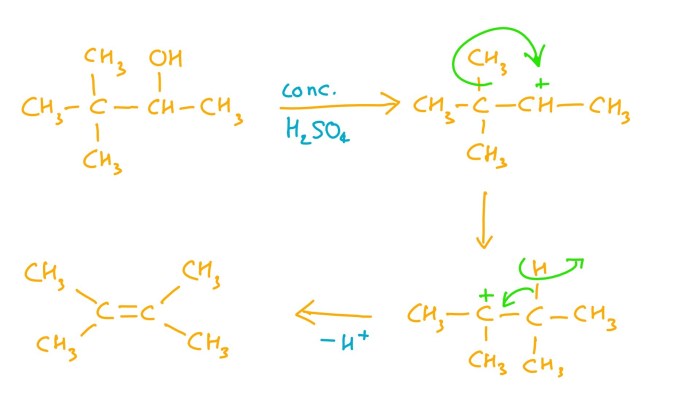
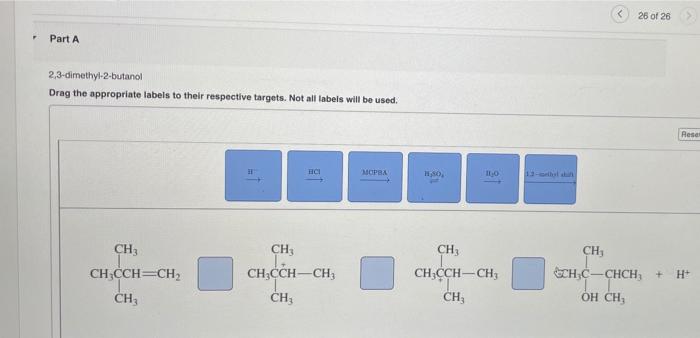
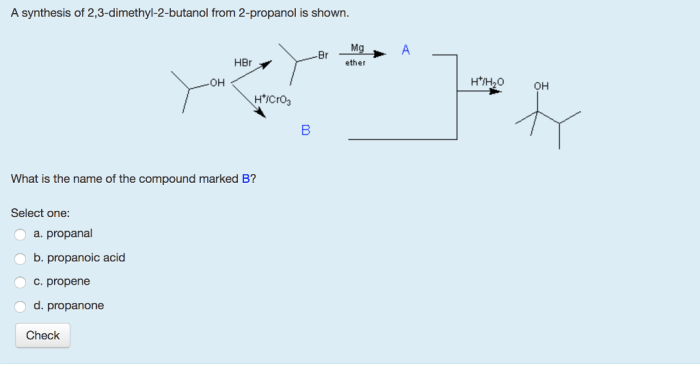
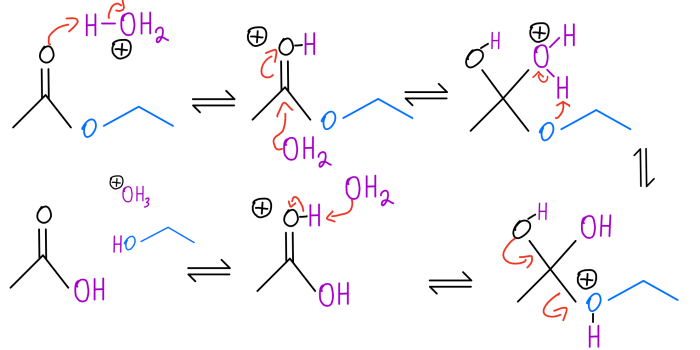
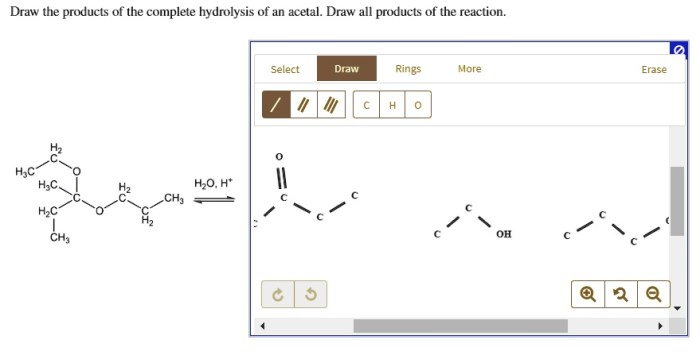
What is the product when this compound undergoes gentle oxidation – Gentle oxidation is a chemical process that involves the addition of oxygen to a compound under mild conditions. This process can result in the formation of a variety of products, depending on the specific compound and the reaction conditions. In this article, we will explore the process of gentle oxidation, identify the products that are formed, and discuss the applications of these products.
When a compound undergoes gentle oxidation, the oxygen atom is typically added to a carbon-carbon double bond, resulting in the formation of an epoxide. Epoxides are three-membered cyclic ethers that are highly reactive and can undergo a variety of reactions.
What is the Product When This Compound Undergoes Gentle Oxidation?
When a compound undergoes gentle oxidation, it reacts with an oxidizing agent under mild conditions to form a more oxidized product. The oxidizing agent typically used is a weak oxidant, such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), and the reaction is carried out at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures.
The process of gentle oxidation can be used to achieve a variety of chemical transformations, including the conversion of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones, the oxidation of alkenes to epoxides, and the oxidative cleavage of double bonds. The conditions and factors that affect gentle oxidation include the strength of the oxidizing agent, the temperature of the reaction, and the presence of catalysts or inhibitors.
Product Identification, What is the product when this compound undergoes gentle oxidation
The product formed when a compound undergoes gentle oxidation depends on the nature of the starting material and the reaction conditions. In general, the product will be more oxidized than the starting material, and it may contain additional oxygen atoms or functional groups.
For example, when an alcohol is oxidized with KMnO4, the product is an aldehyde or ketone. The mechanism of this reaction involves the transfer of two electrons from the alcohol to the oxidizing agent, resulting in the formation of a carbonyl group (C=O).
The physical and chemical properties of the product will also depend on the nature of the starting material and the reaction conditions. In general, the product will be more polar and reactive than the starting material, and it may have a higher boiling point and density.
Applications of the Product
The product formed when a compound undergoes gentle oxidation can be used in a variety of applications, including the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and flavors. For example, the product of the oxidation of an alcohol can be used as a starting material for the synthesis of an ester, which is a common ingredient in perfumes and cosmetics.
The product of the oxidation of an alkene can be used as a starting material for the synthesis of an epoxide, which is a useful intermediate in the synthesis of polymers and pharmaceuticals.
The product of the oxidative cleavage of a double bond can be used as a starting material for the synthesis of two carboxylic acids, which are useful intermediates in the synthesis of a variety of chemicals.
Related Compounds and Reactions
Other compounds that undergo similar oxidation reactions include aldehydes, ketones, and alkenes. The products of these reactions are typically more oxidized than the starting materials, and they may contain additional oxygen atoms or functional groups.
The similarities and differences in the products formed from these reactions depend on the nature of the starting material and the reaction conditions. In general, the products of the oxidation of aldehydes and ketones are more oxidized than the products of the oxidation of alkenes.
The potential for further oxidation or reduction reactions depends on the nature of the product and the reaction conditions. In general, the products of gentle oxidation can be further oxidized or reduced under more vigorous conditions.
Questions Often Asked
What is the difference between gentle oxidation and harsh oxidation?
Gentle oxidation involves the addition of oxygen to a compound under mild conditions, while harsh oxidation involves the addition of oxygen under more vigorous conditions. Harsh oxidation can lead to the formation of a variety of products, including aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids.
What are some examples of compounds that undergo gentle oxidation?
Some examples of compounds that undergo gentle oxidation include alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic compounds.
What are some applications of the products of gentle oxidation?
The products of gentle oxidation have a wide range of applications, including in the production of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and plastics.