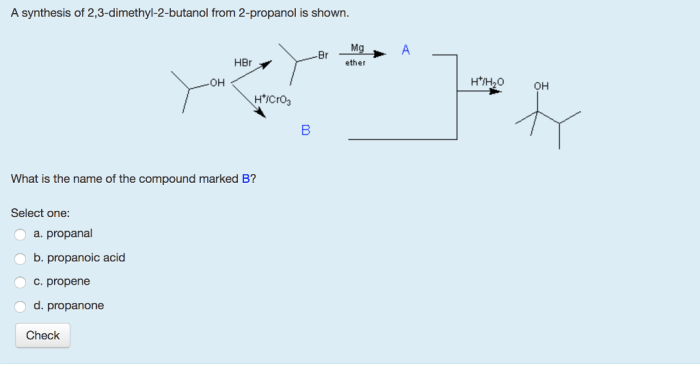
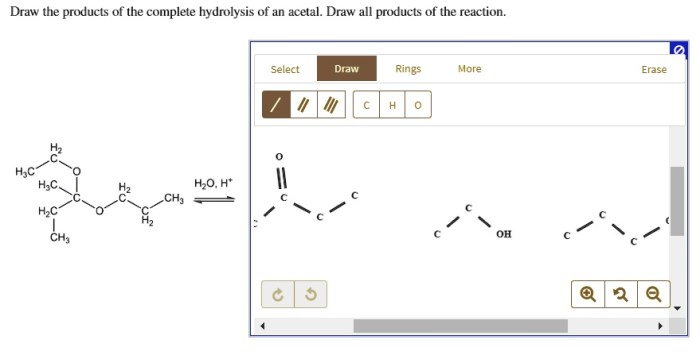
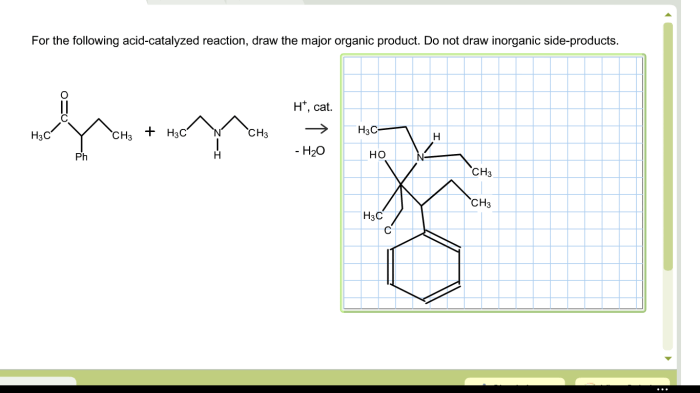
Draw the organic product for the following acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction. Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reactions are a type of chemical reaction in which an acid is used to catalyze the hydrolysis of a compound. Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which water is added to a compound, causing it to break down into its constituent parts.
In acid-catalyzed hydrolysis, the acid protonates the water molecule, making it more reactive and able to attack the compound.
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reactions are used in a variety of industrial applications, including the production of pharmaceuticals, food additives, and other products. They can also be used to recycle or decompose waste materials.
Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis Reaction: Draw The Organic Product For The Following Acid-catalyzed Hydrolysis Reaction.
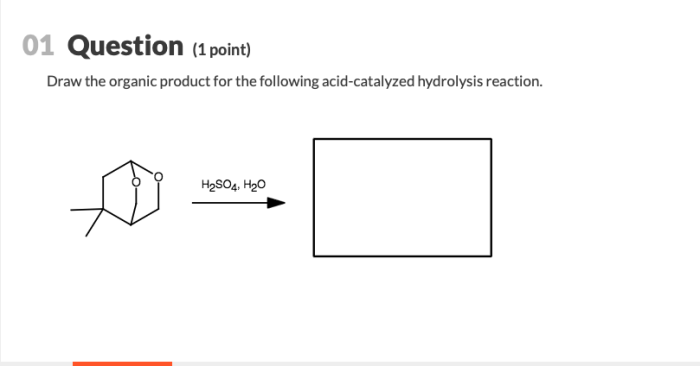
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which a compound reacts with water in the presence of an acid catalyst, resulting in the cleavage of a chemical bond. This reaction is commonly used in organic chemistry to break down complex molecules into simpler ones.
Examples of Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis Reactions
- Hydrolysis of esters to form alcohols and carboxylic acids
- Hydrolysis of amides to form amines and carboxylic acids
- Hydrolysis of glycosides to form sugars and alcohols
Mechanism of Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis Reaction, Draw the organic product for the following acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction.
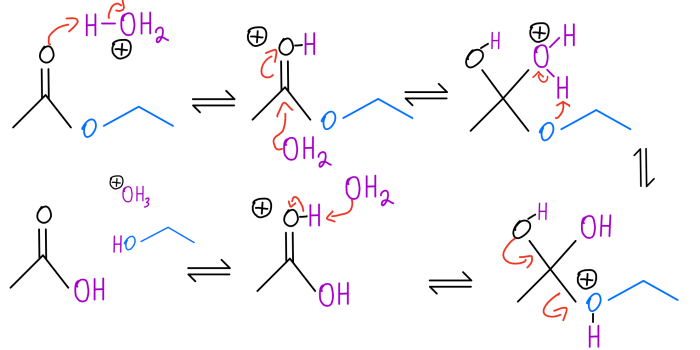
The mechanism of acid-catalyzed hydrolysis involves the following steps:
- Protonation of the substrate by the acid catalyst
- Nucleophilic attack by water on the protonated substrate
- Deprotonation of the intermediate to form the product
Organic Product Identification
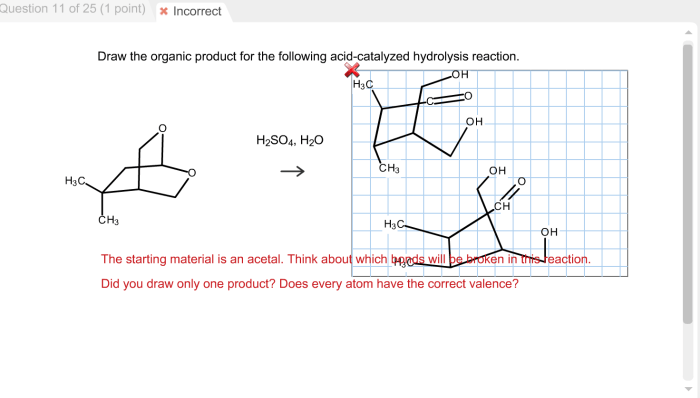
To identify the organic product of an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction, follow these steps:
- Identify the functional group of the substrate.
- Determine the type of acid catalyst used.
- Use the appropriate chemical equation to predict the products.
For example, the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester will produce an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
RCOOR’ + H2O → RCOOH + R’OH
Factors Affecting the Reaction
Several factors can affect the rate and yield of an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase the reaction rate.
- Concentration: Higher concentrations of the substrate and acid catalyst increase the reaction rate.
- Catalyst type: Different acid catalysts have different strengths, which can affect the reaction rate.
| Factor | Effect on Reaction Rate |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Increases |
| Concentration | Increases |
| Catalyst type | Varies depending on catalyst strength |
Applications of Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reactions have various industrial applications:
- Production of pharmaceuticals, such as aspirin and ibuprofen
- Production of food additives, such as citric acid and vinegar
- Recycling of plastics and other waste materials
FAQ Compilation
What is acid-catalyzed hydrolysis?
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis is a type of chemical reaction in which an acid is used to catalyze the hydrolysis of a compound.
What is hydrolysis?
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which water is added to a compound, causing it to break down into its constituent parts.
How do I draw the organic product for an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction?
To draw the organic product for an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction, you need to first identify the functional groups in the reactant molecule. Then, you need to determine which functional group will be hydrolyzed. Once you know which functional group will be hydrolyzed, you can draw the product of the reaction.